Botnet
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
|
|
This article may require copy editing for grammar, style, cohesion, tone, or spelling. You can assist by editing it. (May 2011) |
|
|
This article needs attention from an expert on the subject. See the talk page for details. Consider associating this request with a WikiProject. (May 2011) |
|
|
This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (February 2008) |
Contents[hide] |
[edit] Background
Bots originated as a useful tool without any significant malicious overtone; they were originally developed as a virtual individual that could sit in an IRC channel and perform tasks while the user was too occupied to do so.[2] Soon after the release of the first IRC bot, a few worms which exploited vulnerabilities in IRC clients began to appear. Infected computers, or newly formed "bots", were then used to steal passwords, log keystrokes, and act as a proxy server to conceal the attackers identity.Botnets were used for both recognition and financial gain -- indeed, the larger the botnet, the more ‘kudos’ the person ('bot herder') orchestrating the botnet could claim in underground online communities. The bot herder can also ‘rent out’ the services of the botnet to third parties, usually for sending out spam messages or performing a denial of service attack against a remote target. Due to the large numbers of compromised machines within the botnet, huge volumes of traffic (either email or denial of service) can be generated. However, in recent times, the volume of spam originating from a single compromised host has dropped in order to thwart anti-spam detection algorithms – a larger number of compromised hosts send a smaller number of messages in order to evade detection by anti-spam techniques.
Botnets have become a significant part of the Internet, albeit increasingly hidden. Due to most conventional IRC networks taking measures and blocking access to previously-hosted botnets, controllers must now find their own servers. Often, a botnet will include a variety of connections and network types. Sometimes a controller will hide an IRC server installation on an educational or corporate site where high-speed connections can support a large number of other bots. Exploitation of this method of using a bot to host other bots has proliferated only recently.[citation needed]
Several botnets have been found and removed from the Internet. The Dutch police found a 1.5 million node botnet[3] and the Norwegian ISP Telenor disbanded a 10,000-node botnet.[4] In July 2010, the FBI arrested a 23-year old Slovenian said to have integrated an estimated 12 million computers into a botnet. [5] Large coordinated international efforts to shut down botnets have also been initiated.[6] It has been estimated that botnets control up to 15% of computers worldwide that are connected to the internet.[7] Conficker is one of the largest known botnets, with an estimated 1 million to 10 million infected machines. It attempts to sell fake antivirus software to its victims.[8]
[edit] Recruitment
Computers are recruited into a botnet by running malicious software. This may be achieved by a drive-by download exploiting web browser vulnerabilities, or by tricking the user into running a Trojan horse program, possibly in an email attachment. As with any malware, there is no general rule; the software controls the computer and can do anything. It will typically install modules which allow the computer to be commanded and controlled by the botnet's owner. The Trojan may delete itself, or may remain present to update and maintain the modules.The public warez scene is used to spread malicious software for the recruitment of new bots. Some websites have the malicious software embedded in all their available downloads. There is a false belief among some users, who think that infected keygens are flagged as malicious software by anti-virus programs for only the illegal aspect of the software.
[edit] Organization
While botnets are often named after their malicious software name, there are typically multiple botnets in operation using the same malicious software families, but operated by different criminal entities.[9]While the term "botnet" can be used to refer to any group of bots, such as IRC bots, this word is generally used to refer to a collection of computers (called zombie computers) which have been recruited by running malicious software.
A botnet's originator (aka "bot herder" or "bot master") can control the group remotely, usually through a means such as IRC, and usually for nefarious purposes. Individual programs manifest as IRC "bots". Often the command-and-control takes place via an IRC server or a specific channel on a public IRC network. This server is known as the command-and-control server ("C&C"). Though rare, more experienced botnet operators program their own command protocols from scratch. The constituents of these protocols include a server program, a client program for operation, and the program that embeds itself on the victim's machine (bot). All three of these usually communicate with each other over a network using a unique encryption scheme for stealth and protection against detection or intrusion into the botnet network.
A bot typically runs hidden and uses a covert channel (e.g. the RFC 1459
The architecture of botnets has evolved over time, and not all botnets exhibit the same topology for command and control. Depending upon the topology implemented by the botnet, it may make it more resilient to shutdown, enumeration, or command and control location discovery. However, some of these topologies limit the saleability and rental potential of the botnet to other third-party operators.[11] Typical botnet topologies are:
- Star
- Multi-server
- Hierarchical
- Random
[edit] Formation and exploitation
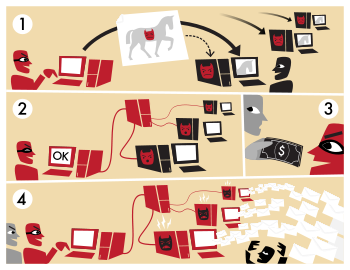
This example illustrates how a botnet is created and used to send email spam.- A botnet operator sends out viruses or worms, infecting ordinary users' computers, whose payload is a malicious application—the bot.
- The bot on the infected PC logs into a particular C&C server (often an IRC server, but, in some cases a web server).
- A spammer purchases the services of the botnet from the operator.
- The spammer provides the spam messages to the operator, who instructs the compromised machines via the IRC server, causing them to send out spam messages.
The botnet controller community features a constant and continuous struggle over who has the most bots, the highest overall bandwidth, and the most "high-quality" infected machines, like university, corporate, and even government machines.[13]
[edit] Types of attacks
- Denial-of-service attacks where multiple systems autonomously access a single Internet system or service in a way that appears legitimate, but much more frequently than normal use and cause the system to become busy.
- Adware exists to advertise some commercial entity actively and without the user's permission or awareness, for example by replacing banner ads on web pages with those of another content provider.
- Spyware is software which sends information to its creators about a user's activities – typically passwords, credit card numbers and other information that can be sold on the black market. Compromised machines that are located within a corporate network can be worth more to the bot herder, as they can often gain access to confidential information held within that company. There have been several targeted attacks on large corporations with the aim of stealing sensitive information, one such example is the Aurora botnet.[14]
- E-mail spam are e-mail messages disguised as messages from people, but are either advertising, annoying, or malicious in nature.
- Click fraud is the user's computer visiting websites without the user's awareness to create false web traffic for the purpose of personal or commercial gain.
- Access number replacements are where the botnet operator replaces the access numbers of a group of dial-up bots to that of a victim's phone number. Given enough bots partaking in this attack, the victim is consistently bombarded with phone calls attempting to connect to the internet. Having very little to defend against this attack, most are forced into changing their phone numbers (land line, cell phone, etc.).
- Fast flux is a DNS technique used by botnets to hide phishing and malware delivery sites behind an ever-changing network of compromised hosts acting as proxies.
- Brute-forcing remote machines services such as FTP, SMTP and SSH.
- The worm behavior. Some botnet are designed to infect other hosts automatically.
- Scareware can install the virus or the virus can install a scareware. For example users can be forced to buy a rogue anti-virus to regain access to their computer.[15]
- Exploiting systems by using multiple identities such as multiple player at the same poker table and voting system such as music clip and contest.[16]
[edit] Preventive measures
If a machine receives a denial-of-service attack from a botnet, few choices exist. Given the general geographic dispersal of botnets, it becomes difficult to identify a pattern of offending machines, and the sheer volume of IP addresses does not lend itself to the filtering of individual cases. Passive OS fingerprinting can identify attacks originating from a botnet: network administrators can configure newer firewall equipment to take action on a botnet attack by using information obtained from passive OS fingerprinting. The most serious preventive measures utilize rate-based intrusion prevention systems implemented with specialized hardware. A network based intrusion detection system (NIDS) will be an effective approach when detecting any activities approaching botnet attacks. NIDS monitors a network, it sees protected hosts in terms of the external interfaces to the rest of the network, rather than as a single system, and get most of its results by network packet analysis.[17]Some botnets use free DNS hosting services such as DynDns.org, No-IP.com, and Afraid.org to point a subdomain towards an IRC server that will harbor the bots. While these free DNS services do not themselves host attacks, they provide reference points (often hard-coded into the botnet executable). Removing such services can cripple an entire botnet. Recently, these companies have undertaken efforts to purge their domains of these subdomains. The botnet community refers to such efforts as "nullrouting", because the DNS hosting services usually re-direct the offending subdomains to an inaccessible IP address. Similarly, some botnets implement custom versions of well-known protocols. The implementation differences can be used for fingerprint-based detection of botnets. For example, Mega-D features a slightly modified SMTP protocol implementation for testing the spam capability. Bringing down the Mega-D's SMTP server disables the entire pool of bots that rely upon the same SMTP server.[18]
The botnet server structure mentioned above has inherent vulnerabilities and problems. For example, if one was to find one server with one botnet channel, often all other servers, as well as other bots themselves, will be revealed. If a botnet server structure lacks redundancy, the disconnection of one server will cause the entire botnet to collapse, at least until the controller(s) decide on a new hosting space. However, more recent IRC server software includes features to mask other connected servers and bots, so that a discovery of one channel will not lead to disruption of the botnet.
Several security companies such as Afferent Security Labs, Symantec, Trend Micro, FireEye, Umbra Data and Damballa have announced offerings to stop botnets. While some, like Norton AntiBot (discontinued), are aimed at consumers, most are aimed to protect enterprises and/or ISPs. The host-based techniques use heuristics to try to identify bot behavior that has bypassed conventional anti-virus software. Network-based approaches tend to use the techniques described above; shutting down C&C servers, nullrouting DNS entries, or completely shutting down IRC servers.
Newer botnets are almost entirely P2P, with command-and-control embedded into the botnet itself. By being dynamically updateable and variable they can evade having any single point of failure. Commanders can be identified solely through secure keys and all data except the binary itself can be encrypted. For example a spyware program may encrypt all suspected passwords with a public key hard coded or distributed into the bot software. Only with the private key, which only the commander has, can the data that the bot has captured be read.
Newer botnets have even been capable of detecting and reacting to attempts to figure out how they work. A large botnet that can detect that it is being studied can even DDoS those studying it off the internet.
There is an effort by researchers at Sandia National Laboratories to analyze the behavior of these botnets by simultaneously running one million Linux kernels as virtual machines on a 4,480-node Dell high-performance computer cluster.[19]
[edit] Historical list of botnets
| Date created | Date dismantled | Name | Estimated no. of bots | Spam capacity | Aliases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 (May) | BredoLab | 30,000,000[20] | 3.6 billion/day | Oficla | |
| 2008 (around) | Mariposa | 12,000,000[21] | ? | ||
| ? | Conficker | 10,500,000+[22] | 10 billion/day | DownUp, DownAndUp, DownAdUp, Kido | |
| 2010 (around) | TDL4 | 4,500,000[23] | ? | TDSS, Alureon | |
| ? | Zeus | 3,600,000 (US Only) [24] | n/a | Zbot, PRG, Wsnpoem, Gorhax, Kneber | |
| 2007 (Around) | Cutwail | 1,500,000 [25] | 74 billion/day | Pandex, Mutant (related to: Wigon, Pushdo) | |
| 2008 (Around) | Sality | 1,000,000 [26] | ? | Sector, Kuku | |
| ? | Grum | 560,000 [27] | 39.9 billion/day | Tedroo | |
| ? | Mega-D | 509,000 [28] | 10 billion/day | Ozdok | |
| ? | Kraken | 495,000 [29] | 9 billion/day | Kracken | |
| 2007 (March) | Srizbi | 450,000[30] | 60 billion/day | Cbeplay, Exchanger | |
| ? | Lethic | 260,000 [31] | 2 billion/day | none | |
| 2004 (Early) | Bagle | 230,000[31] | 5.7 billion/day | Beagle, Mitglieder, Lodeight | |
| ? | Bobax | 185,000[31] | 9 billion/day | Bobic, Oderoor, Cotmonger, Hacktool.Spammer, Kraken | |
| ? | Torpig | 180,000 [32] | n/a | Sinowal, Anserin | |
| ? | Storm | 160,000 [33] | 3 billion/day | Nuwar, Peacomm, Zhelatin | |
| 2006 (Around) | Rustock | 150,000 [34] | 30 billion/day | RKRustok, Costrat | |
| ? | Donbot | 125,000 [35] | 0.8 billion/day | Buzus, Bachsoy | |
| 2008 (November) | Waledac | 80,000 [36] | 1.5 billion/day | Waled, Waledpak | |
| ? | Maazben | 50,000 [31] | 0.5 billion/day | None | |
| ? | Onewordsub | 40,000 [37] | 1.8 billion/day | ? | |
| ? | Gheg | 30,000 [31] | 0.24 billion/day | Tofsee, Mondera | |
| ? | ?? | 20,000 [37] | 5 billion/day | Loosky, Locksky | |
| ? | Wopla | 20,000 [37] | 0.6 billion/day | Pokier, Slogger, Cryptic | |
| 2008 (Around) | Asprox | 15,000 [38] | ? | Danmec, Hydraflux | |
| Spamthru | 12,000 [37] | 0.35 billion/day | Spam-DComServ, Covesmer, Xmiler | ||
| 2010 (January) | LowSec | 11,000+ [31] | 0.5 billion/day | LowSecurity, FreeMoney, Ring0.Tools | |
| ? | Xarvester | 10,000 [31] | 0.15 billion/day | Rlsloup, Pixoliz | |
| 2009 (August) | Festi | ? | 2.25 billion/day | none | |
| 2008 (Around) | Gumblar | ? | ? | None | |
| 2007 | Akbot | 1,300,000 [39] | ? | None |
- Researchers at the University of California, Santa Barbara took control of a botnet that was six times smaller than expected. In some countries, it is common that users change their IP address a few times in one day. Estimating the size of the botnet by the number of IP addresses is often used by researchers, possibly leading to inaccurate assessments.[40]
No comments:
Post a Comment